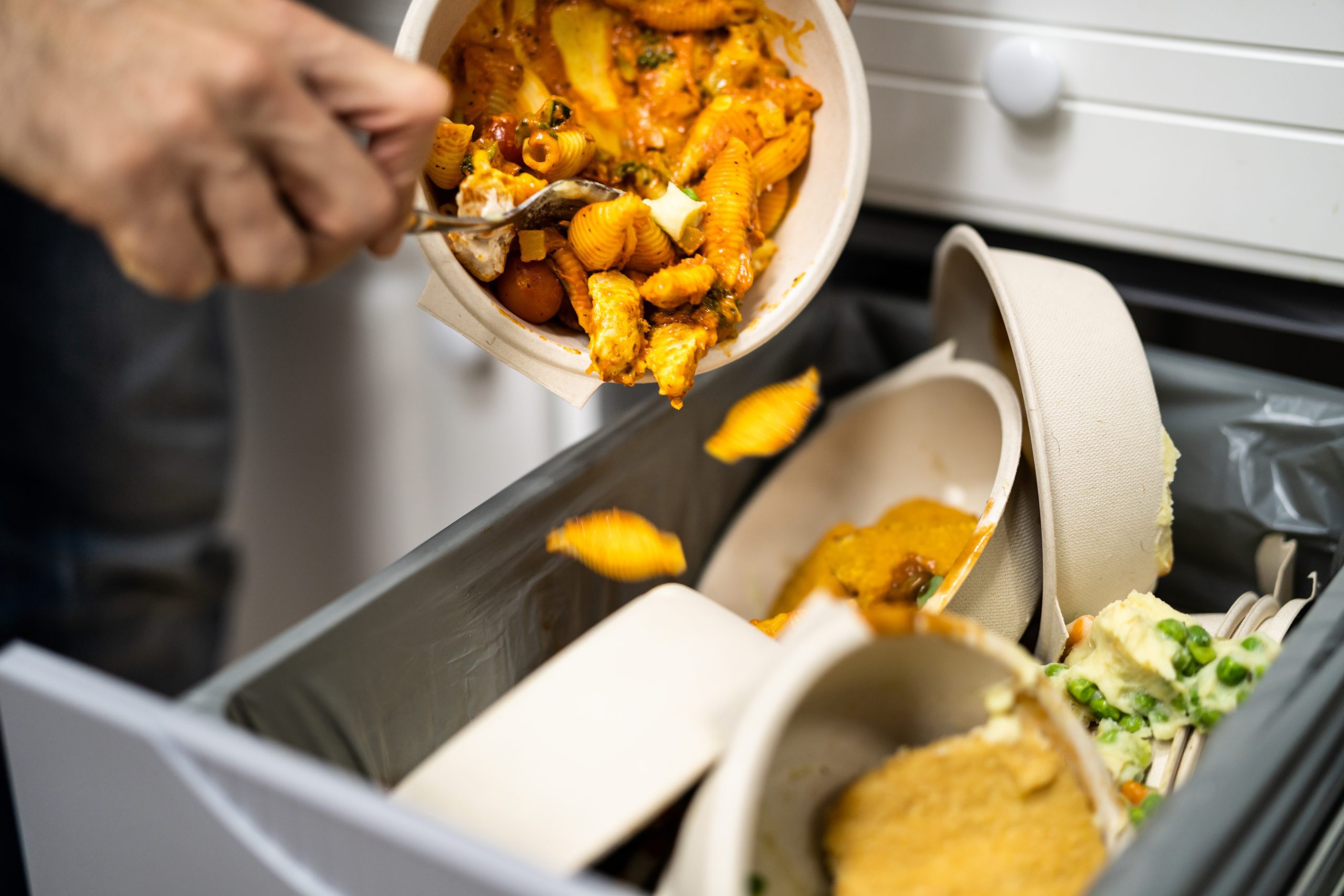
In a world grappling with enormous environmental challenges and food insecurity, tackling food waste has emerged as a crucial endeavor. This article therefore explores the significance of this topic and highlights the innovative technologies and approaches from industry players aimed at curbing food waste. From minimizing environmental impact to addressing global hunger, food waste reduction holds immense potential for creating a sustainable future.
Introduction
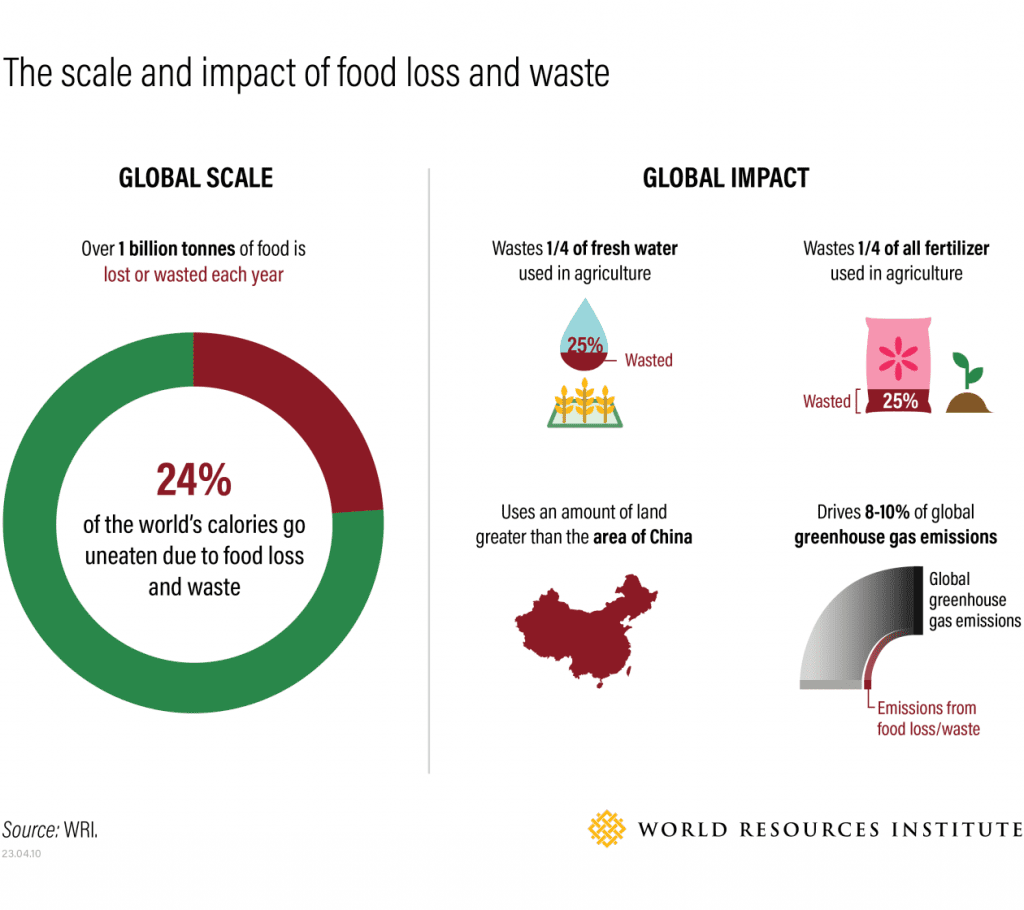
Food waste occurs along the entire spectrum of production – from the farm to distribution to retailers to the consumer. We throw out a third of the food we produce globally – 1.3 billion tons per year, to be precise. More so, if current trends persist, food loss and waste will double by 2050. When you consider that nearly one billion people go hungry each year, this waste is especially egregious. When scraps end up in landfills, it decomposes and emits greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide and methane. Estimates suggest that 8-10% of global greenhouse gas emissions are associated with food that is not consumed. To put this into perspective, if global food waste were a country, it would be the third largest emitter of carbon dioxide after the United States and China. Thus, according to a report by UN Environment Programme, reducing food waste could save USD 300 billion annually.
It is therefore no surprise that food waste reduction has gained traction as a vital solution in combating environmental degradation and resource depletion. The economic, social, and environmental implications are significant. The reduction of food scraps can thus create a profound market impact by reducing environmental strain and providing economic opportunities worth billions of dollars through resource optimization and cost savings.
Benefits of Food Waste Reduction
- Conservation of Natural Resources: It helps conserve natural resources by reducing the need for land, water, and energy in food production.
- Minimized Greenhouse Gas Emissions: It minimizes greenhouse gas emissions associated with food decomposition in landfills. Thus, estimates indicate that a total elimination of scraps can lead to a reduction of 8-10% of global greenhouse gas emissions.
- Food Security: By redirecting surplus food to those in need, it addresses food insecurity and fosters social equity.
- Economic Cost-Saving: Finally, businesses and households can save substantial costs by minimizing waste.
Source: WRI
Risks and Potential Solutions
- Logistical Complexities: Managing food waste reduction initiatives involves complex logistics, especially in large-scale systems like supply chains, distribution networks, and refuse management. Coordinating the collection, transportation, and processing of surplus food items requires efficient planning and collaboration among stakeholders.
- Inadequate Infrastructure: Insufficient infrastructure, such as proper disposal facilities, composting sites, or recycling centers, can impede effective food waste reduction efforts. The lack of appropriate facilities for handling and processing these wastes hampers the ability to manage it sustainably.
- Lack of Awareness: Limited awareness about the consequences of wasting food at various stages of the supply chain contributes to the problem. Stakeholders, including producers, retailers, and consumers, may however not fully comprehend the environmental, social, and economic impacts of wastage.
- Consumer Behavior: Consumer behavior plays a significant role in contributing to food loss. Practices such as overbuying, improper storage, and discarding edible food due to cosmetic imperfections or expiry dates contribute to the issue. Therefore, changing consumer habits and educating individuals about mindful consumption are crucial for reducing waste.
Overcoming these hurdles requires collaborative efforts, including improved supply chain management, enhanced public education campaigns, investment in waste processing facilities, and policy support from governments.
Main Startups in the Field
Numerous organizations and initiatives are actively engaged in excess food reduction. Notable players include non-profit organizations like Food Forward which fights hunger and prevents excess food by rescuing fresh surplus produce, connecting this abundance with people experiencing food insecurity, and inspiring others to do the same. There are also technology-driven companies and start-ups that are offering innovative solutions, from waste-tracking systems to natural food preservation technologies. For instance, Winnow, a waste-reduction technology company, develops technology for chefs that collects and analyses daily waste. Other notable technology-driven companies include Apeel Sciences, TripleW, BIOCHP, Replate, Flyfarm etc.

Explore all Key Players:
Example Case Study
One inspiring case study is the partnership between Gomez, a fresh produce business and FareShare, a charity organisation. Each year, surplus groceries that would have otherwise gone to waste becomes donations. For instance, reports indicated that in 2020, this partnership facilitated the donation of over 29 tonnes of surplus food.
Takeaway
Food waste reduction is not just an environmental imperative; it is a responsibility shared by individuals, businesses, and governments worldwide. By adopting sustainable practices, investing in innovative technologies, and fostering collaborative initiatives, we can make a tangible difference. Together, we can build a future where wasting of food is minimized, resources are optimized, and hunger is alleviated, ensuring a greener and more sustainable world for generations to come.
Explore related topics
- Agriculture & Forestry Posts
- Aquaculture Posts
- Bio-based Product Posts
- Bio-Resource Conversion Industry Posts
- Blog
- CO2 & Waste Utilization Posts
- Food & Beverage Posts
- Water & Renewable Energy Posts


