As the global population soars and arable land diminishes, the agricultural sector faces a pivotal challenge. Vertical farming emerges as a powerful tool, transforming food production with its innovative approach towards more sustainability.
Introduction
In view of the global population increase, the conventional landscape of agriculture is facing unprecedented challenges. With a predicted increase of 60% in required food by 2050, the need for innovative solutions is very apparent. This brings us to a new chapter of agricultural evolution – vertical farming.
At its essence, vertical farming represents a departure from traditional agricultural practices, pursue a three-dimensional approach to cultivation. In the conventional agricultural paradigm, the expansion of arable land is limited by finite resources and environmental concerns. Still, this presents a revolutionary subset of precision agriculture that transforms the traditional horizontal expanse into a vertical plane. With accuracy at its core, inputs are carefully optimized and managed. Likewise, this method goes beyond the conventional boundaries of soil-based cultivation, which eliminates the need for traditional soil. Therefore, plants are able to thrive in carefully controlled environments, increasing efficiency and reducing the amount of waste.
Relevancy Growing to New Heights
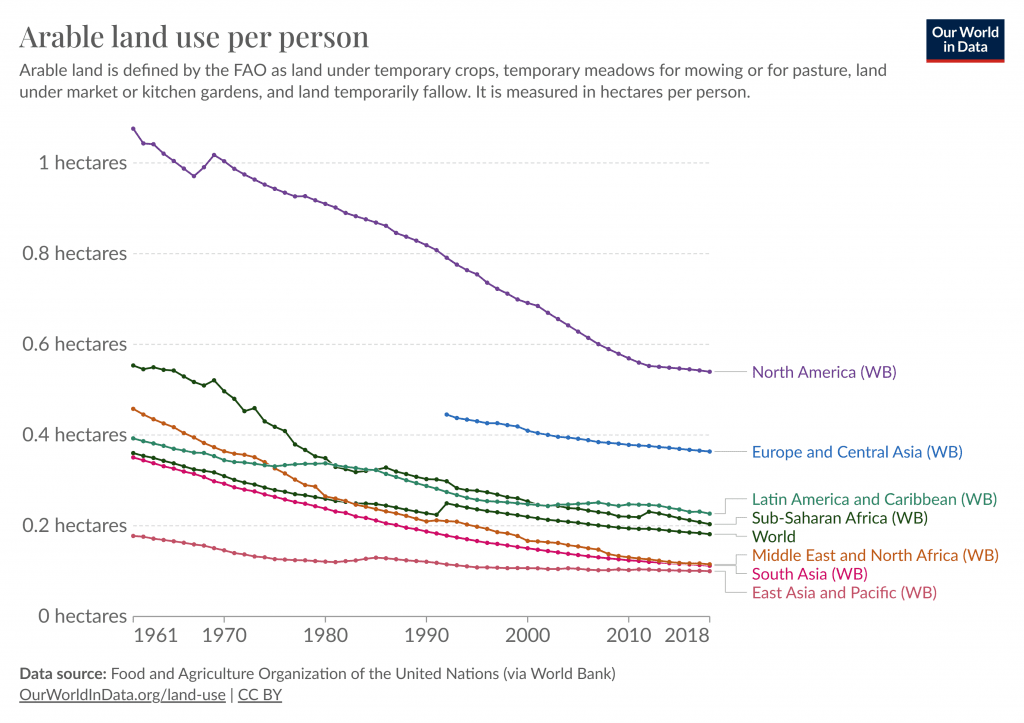
As vertical farming techniques become increasingly sophisticated, it becomes clear that this innovative approach is not merely a trend. It is a necessity dictated by the limitations of our current agricultural trajectory. Correspondingly, arable land projections, as stated by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), suggest a mere 2% increase by 2040, which demonstrates the urgency of a paradigm shift. Therefore, with traditional horizontal expansion reaching its limits, and with arable land facing constraints, the path to meeting future food demands must shift upwards. This pivotal shift in perspective not only addresses the challenges posed by the lack of land but also opens doors to a new era of efficiency and resource improvement.
Furthermore, the financial landscape speaks volumes about the confidence placed in Vertical Farming as a transformative force in agriculture. Vertical farming ventures attracted over $1 billion USD in funding over the past decade. Hence, it is evident that the world recognizes the economic viability and potential impact of vertical farming. This substantial investment is not merely a financial endorsement. It signifies a collective belief that vertical farming is not just a fleeting trend but a strategic investment in the future of food production. As startups, corporations, and investors rally behind vertical farming, the economic ripple effect extends beyond profitability. Now, it has become a testament to the broader societal recognition of vertical farming’s crucial role in redefining the way we cultivate, harvest, and sustain ourselves.
Nurturing the Seeds of Vertical Farming
- Land Use Efficiency: Vertical farming’s ability to cultivate crops in stacked layers significantly reduces the land footprint compared to traditional farming methods. In a world where arable land is becoming increasingly scarce, this efficiency is crucial to feed the growing global population. Intensive farming has historically led to environmental degradation, but vertical farming offers a promising solution by increasing productivity in a smaller spatial footprint.
- Nutrient Optimization: Vertical farming systems often employ hydroponics or aeroponics, eliminating the need for traditional soil. This precision agriculture technique allows for optimal control of nutrient delivery to plants, ensuring they receive what they need for optimal growth. Therefore, by circumventing the limitations and risks associated with cultivation based on soil, vertical farming enhances nutrient efficiency, leading to higher yields and reduced waste.
- Energy Efficiency: In certain contexts, Vertical farming exhibits the potential to be more energy-efficient compared to traditional farms. Using technologies like light-emitting diodes (LEDs), vertical farming can anhance the light spectrum and duration, to improve energy consumption. Although initial setup costs may be higher, the long-term benefits of reduced energy usage contribute to a more environmentally friendly farming model.

Navigating the Challenge of Vertical Farms
- Limited Crop Variety: One of the primary weaknesses of vertical farming lies in the limited range of crops suitable for this method. These farming conditions are most conducive to leafy vegetables and small fruits, excluding vital crops like sugar cane, wheat, and maize. Consequently, the inability to accommodate a broader spectrum of crops hampers its potential to replace traditional farming entirely. This is especially apparent given the global dependence on staple crops not currently implemented in vertical farming systems.
- Dependency on Technology: The success is intricately tied to technology, particularly in terms of climate control, lighting, and automation. While technology enhances efficiency, it also introduces vulnerabilities. Dependency on a complex technological infrastructure makes vertical farming systems susceptible to disruptions, from power outages, system failures, or cyber threats. Hence, this reliance poses a potential risk to the consistency and reliability of operations.
- Economic Viability and High Initial Costs: Despite the significant funding vertical farming ventures have attracted, the combined startup and operational costs can be prohibitively expensive. The need for specialized infrastructure, advanced technologies, and controlled environments contributes to high initial investment. For vertical farming to be seamlessly integrated into conventional farming practices, it must demonstrate sustained profitability. Thus, economic viability remains a challenge, especially for smaller-scale operations or in regions where capital investment is difficult to receive.
Skyrocketing Startups in the Field
Vertical Future: Cultivating Sustainable Solutions
Vertical Future turns out to be an innovative startup that points the way toward sustainable and efficient food production. With a mission to address the challenges posed by traditional agriculture, Vertical Future pioneers their approach to farming within urban environments. Utilizing advanced technologies like hydroponics and aeroponics, Vertical Future optimizes nutrient delivery, reducing waste and environmental impact. Their innovative use of vertical spaces, coupled with a commitment to precision agriculture, positions the vertical future at the forefront of the urban farming revolution.
What sets Vertical Future apart is both its commitment to sustainability and holistic approach to address global food security issues. By focusing on nutrient improvement and energy efficiency, Vertical Future creates a blueprint for urban farming that goes beyond the immediate need for increased food production. Its integration of technology and sustainable practices not only addresses the limitations of traditional agriculture but also sets a new standard for the future of food cultivation in urban environments.
AeroFarms: Elevating Agriculture to New Heights
AeroFarms stands as an industry heavyweight, revolutionizing the way we think about and produce food. This Newark-based startup has redefined traditional farming by transforming unused industrial spaces into thriving vertical farms. They employ a unique aeroponic system that delivers nutrients directly to plant roots, optimizing growth and resource usage. With a commitment to sustainability, this pioneering startup sets new benchmarks for energy efficiency through the use of cutting-edge technologies like LED lighting, saving a more sustainable future for agriculture.
Moreover, AeroFarms not only boasts technological innovation but also emphasizes community impact. By locating in urban areas, AeroFarms reduces the carbon footprint associated with food transportation. Furthermore, this makes fresh produce more accessible to local communities. The startup’s commitment to social responsibility aligns seamlessly with its technological, creating a comprehensive model for the future of agriculture. Indeed, AeroFarms continues to receive industry recognition, demonstrating that profitability and sustainability can thrive hand in hand with vertical farming.
Explore all Key Players in CEA:
Cultivating Tomorrow: The Vertical Farming Paradigm
In conclusion, vertical farming emerges as a revolutionary solution to the challenges posed by traditional agriculture. Its sustainable methods offer a path towards increased food production and resource improvement. While limitations exist, the immense potential and ongoing investments signal a promising future for vertical farming. Hence, the strengths of vertical farming paint a picture where the sky is the limit for food production.
The towering stacks of farms gives a narrative of innovation, sustainability, and agricultural evolution unfolds. Vertical farming overcomes the limitations of traditional agriculture and offers a three-dimensional solution to the challenges we face. As startups, corporates, and investors explore its profitability, it becomes clear to embrace innovation for a more sustainable and secure global food supply.
Explore related topics
- Agriculture & Forestry Posts
- Aquaculture Posts
- Bio-based Product Posts
- Bio-Resource Conversion Industry Posts
- Blog
- CO2 & Waste Utilization Posts
- Food & Beverage Posts
- Water & Renewable Energy Posts
Sources:
- https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Opportunities-and-Challenges-in-Sustainability-of-A-Kalantari-Tahir/d333c98f059ca6ebfb53b8faae95291ff63732cd
- https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/14620316.2022.2141666
- https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1755-1315/256/1/012050
- https://khu.elsevierpure.com/en/publications/trait-improvement-of-solanaceae-fruit-crops-for-vertical-farming-
- https://verticalfuture.com/
- https://www.aerofarms.com/


